Callbacks: Observe, Customize, and Control Agent Behavior¶
回调:观察、自定义和控制智能体行为¶
Callbacks are a cornerstone feature of ADK, providing a powerful mechanism to hook into an agent's execution process. They allow you to observe, customize, and even control the agent's behavior at specific, predefined points without modifying the core ADK framework code.
回调是 ADK 的核心功能,提供了一个强大的机制来挂钩到智能体的执行过程。它们允许您在不修改核心 ADK 框架代码的情况下,在特定的预定义点观察、自定义甚至控制智能体的行为。
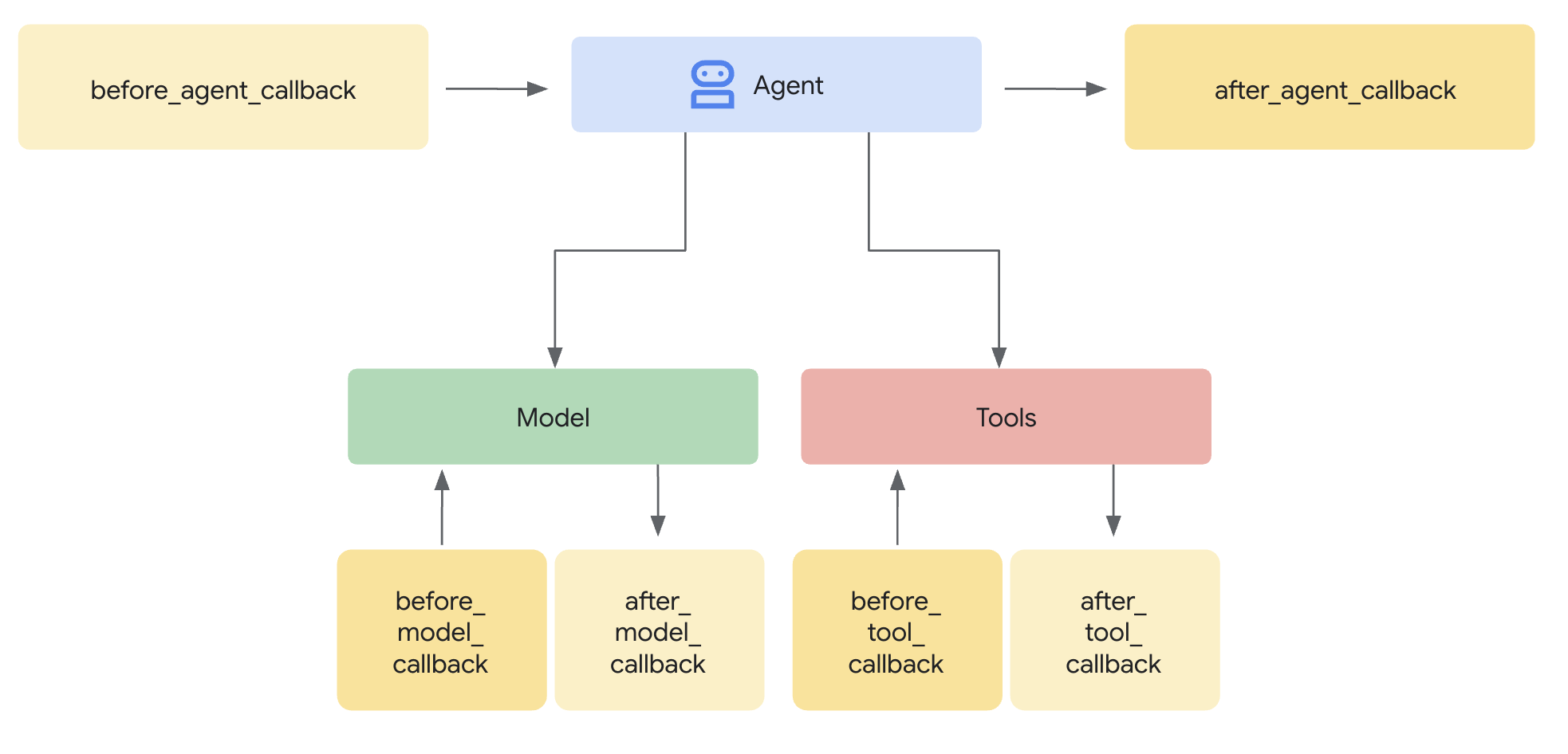
What are they? In essence, callbacks are standard functions that you define. You then associate these functions with an agent when you create it. The ADK framework automatically calls your functions at key stages, letting you observe or intervene. Think of it like checkpoints during the agent's process:
它们是什么?本质上,回调是您定义的标准函数。您在创建智能体时将这些函数与智能体关联。ADK 框架在关键阶段自动调用您的函数,让您观察或干预。可以将其视为智能体过程中的检查点:
- Before the agent starts its main work on a request, and after it finishes: When you ask an agent to do something (e.g., answer a question), it runs its internal logic to figure out the response.
- The
Before Agentcallback executes right before this main work begins for that specific request. - The
After Agentcallback executes right after the agent has finished all its steps for that request and has prepared the final result, but just before the result is returned. -
This "main work" encompasses the agent's entire process for handling that single request. This might involve deciding to call an LLM, actually calling the LLM, deciding to use a tool, using the tool, processing the results, and finally putting together the answer. These callbacks essentially wrap the whole sequence from receiving the input to producing the final output for that one interaction.
-
在智能体开始处理请求的主要工作之前和处理完成之后**:当您要求智能体执行某项操作(例如,回答问题)时,它会运行其内部逻辑来计算响应。
Before Agent回调在该特定请求的主要工作开始之前执行。After Agent回调在智能体完成该请求的所有步骤并准备最终结果但尚未返回结果之后执行。- 这个"主要工作"涵盖智能体处理该单个请求的整个过程。这可能涉及决定调用 LLM、实际调用 LLM、决定使用工具、使用工具、处理结果以及最终组合答案。这些回调本质上将从接收输入到为该交互产生最终输出的整个序列包裹起来。
- Before sending a request to, or after receiving a response from, the Large Language Model (LLM): These callbacks (
Before Model,After Model) allow you to inspect or modify the data going to and coming from the LLM specifically. -
Before executing a tool (like a Python function or another agent) or after it finishes: Similarly,
Before ToolandAfter Toolcallbacks give you control points specifically around the execution of tools invoked by the agent. -
在向大语言模型 (LLM)发送请求之前或从其接收响应之后:这些回调(
Before Model、After Model)允许您专门检查或修改发送到 LLM 和从 LLM 接收的数据。 - 在执行工具(如 Python 函数或另一个智能体)之前或完成之后:同样,
Before Tool和After Tool回调专门为智能体调用的工具执行提供控制点。
Why use them? Callbacks unlock significant flexibility and enable advanced agent capabilities:
为什么要使用它们? 回调解锁了巨大的灵活性并实现了高级智能体功能:
- Observe & Debug: Log detailed information at critical steps for monitoring and troubleshooting.
- Customize & Control: Modify data flowing through the agent (like LLM requests or tool results) or even bypass certain steps entirely based on your logic.
- Implement Guardrails: Enforce safety rules, validate inputs/outputs, or prevent disallowed operations.
- Manage State: Read or dynamically update the agent's session state during execution.
-
Integrate & Enhance: Trigger external actions (API calls, notifications) or add features like caching.
-
观察和调试: 在关键步骤记录详细信息以进行监控和故障排除。
- 自定义和控制: 修改流经智能体的数据(如 LLM 请求或工具结果),或者根据您的逻辑完全绕过某些步骤。
- 实施防护栏: 强制执行安全规则、验证输入/输出或防止不允许的操作。
- 管理状态: 在执行期间读取或动态更新智能体的会话状态。
- 集成和增强: 触发外部操作(API 调用、通知)或添加缓存等功能。
Tip
When implementing security guardrails and policies, use ADK Plugins for better modularity and flexibility than Callbacks. For more details, see Callbacks and Plugins for Security Guardrails.
How are they added:
如何添加它们:
Code
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from typing import Optional
# --- Define your callback function ---
def my_before_model_logic(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
print(f"Callback running before model call for agent: {callback_context.agent_name}")
# ... your custom logic here ...
return None # Allow the model call to proceed
# --- Register it during Agent creation ---
my_agent = LlmAgent(
name="MyCallbackAgent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash", # Or your desired model
instruction="Be helpful.",
# Other agent parameters...
before_model_callback=my_before_model_logic # Pass the function here
)
import {
LlmAgent,
InMemoryRunner,
CallbackContext,
LlmRequest,
LlmResponse,
Event,
isFinalResponse,
} from "@google/adk";
import { createUserContent } from "@google/genai";
import type { Content } from "@google/genai";
const MODEL_NAME = "gemini-2.5-flash";
const APP_NAME = "basic_callback_app";
const USER_ID = "test_user_basic";
const SESSION_ID = "session_basic_001";
// --- Define your callback function ---
function myBeforeModelLogic({
context,
request,
}: {
context: CallbackContext;
request: LlmRequest;
}): LlmResponse | undefined {
console.log(
`Callback running before model call for agent: ${context.agentName}`
);
// ... your custom logic here ...
return undefined; // Allow the model call to proceed
}
// --- Register it during Agent creation ---
const myAgent = new LlmAgent({
name: "MyCallbackAgent",
model: MODEL_NAME,
instruction: "Be helpful.",
beforeModelCallback: myBeforeModelLogic,
});
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// onBeforeModel is a callback function that gets triggered before an LLM call.
func onBeforeModel(ctx agent.CallbackContext, req *model.LLMRequest) (*model.LLMResponse, error) {
log.Println("--- onBeforeModel Callback Triggered ---")
log.Printf("Model Request to be sent: %v\n", req)
// Returning nil allows the default LLM call to proceed.
return nil, nil
}
func runBasicExample() {
const (
appName = "CallbackBasicApp"
userID = "test_user_123"
)
ctx := context.Background()
geminiModel, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
// Register the callback function in the agent configuration.
agentCfg := llmagent.Config{
Name: "SimpleAgent",
Model: geminiModel,
BeforeModelCallbacks: []llmagent.BeforeModelCallback{onBeforeModel},
}
simpleAgent, err := llmagent.New(agentCfg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: simpleAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
import com.google.adk.agents.CallbackContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.Callbacks;
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmRequest;
import java.util.Optional;
public class AgentWithBeforeModelCallback {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// --- Define your callback logic ---
Callbacks.BeforeModelCallbackSync myBeforeModelLogic =
(CallbackContext callbackContext, LlmRequest llmRequest) -> {
System.out.println(
"Callback running before model call for agent: " + callbackContext.agentName());
// ... your custom logic here ...
// Return Optional.empty() to allow the model call to proceed,
// similar to returning None in the Python example.
// If you wanted to return a response and skip the model call,
// you would return Optional.of(yourLlmResponse).
return Optional.empty();
};
// --- Register it during Agent creation ---
LlmAgent myAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("MyCallbackAgent")
.model("gemini-2.0-flash") // Or your desired model
.instruction("Be helpful.")
// Other agent parameters...
.beforeModelCallbackSync(myBeforeModelLogic) // Pass the callback implementation here
.build();
}
}
The Callback Mechanism: Interception and Control¶
回调机制:拦截和控制¶
When the ADK framework encounters a point where a callback can run (e.g., just before calling the LLM), it checks if you provided a corresponding callback function for that agent. If you did, the framework executes your function.
当 ADK 框架遇到可以运行回调的点(例如,就在调用 LLM 之前)时,它会检查您是否为该智能体提供了相应的回调函数。如果提供了,框架将执行您的函数。
Context is Key: Your callback function isn't called in isolation. The framework provides special context objects (CallbackContext or ToolContext) as arguments. These objects contain vital information about the current state of the agent's execution, including the invocation details, session state, and potentially references to services like artifacts or memory. You use these context objects to understand the situation and interact with the framework. (See the dedicated "Context Objects" section for full details).
上下文是关键: 您的回调函数不是在隔离中调用的。框架提供特殊的上下文对象(CallbackContext 或 ToolContext)作为参数。这些对象包含有关智能体执行当前状态的重要信息,包括调用详细信息、会话状态,以及对工件或内存等服务的潜在引用。您使用这些上下文对象来了解情况并与框架交互。(有关详细信息,请参阅专门的"上下文对象"部分)。
Controlling the Flow (The Core Mechanism): The most powerful aspect of callbacks lies in how their return value influences the agent's subsequent actions. This is how you intercept and control the execution flow:
控制流程(核心机制): 回调最强大的方面在于它们的返回值如何影响智能体的后续操作。这就是您拦截和控制执行流程的方式:
-
return None(Allow Default Behavior):- The specific return type can vary depending on the language. In Java, the equivalent return type is
Optional.empty(). Refer to the API documentation for language specific guidance. - This is the standard way to signal that your callback has finished its work (e.g., logging, inspection, minor modifications to mutable input arguments like
llm_request) and that the ADK agent should proceed with its normal operation. - For
before_*callbacks (before_agent,before_model,before_tool), returningNonemeans the next step in the sequence (running the agent logic, calling the LLM, executing the tool) will occur. - For
after_*callbacks (after_agent,after_model,after_tool), returningNonemeans the result just produced by the preceding step (the agent's output, the LLM's response, the tool's result) will be used as is.
- The specific return type can vary depending on the language. In Java, the equivalent return type is
-
return None(允许默认行为):- 具体的返回类型可能因语言而异。在 Java 中,等效的返回类型是
Optional.empty()。请参阅 API 文档以获取特定语言的指导。 - 这是发出回调已完成工作(例如,记录、检查、对可变输入参数(如
llm_request)进行轻微修改)的信号,并且 ADK 智能体应该继续其正常操作的标准方式。 - 对于
before_*回调(before_agent、before_model、before_tool),返回None意味着序列中的下一步(运行智能体逻辑、调用 LLM、执行工具)将发生。 - 对于
after_*回调(after_agent、after_model、after_tool),返回None意味着上一步产生的结果(智能体的输出、LLM 的响应、工具的结果)将按原样使用。
- 具体的返回类型可能因语言而异。在 Java 中,等效的返回类型是
-
return <Specific Object>(Override Default Behavior):- Returning a specific type of object (instead of
None) is how you override the ADK agent's default behavior. The framework will use the object you return and skip the step that would normally follow or replace the result that was just generated. before_agent_callback→types.Content: Skips the agent's main execution logic (_run_async_impl/_run_live_impl). The returnedContentobject is immediately treated as the agent's final output for this turn. Useful for handling simple requests directly or enforcing access control.before_model_callback→LlmResponse: Skips the call to the external Large Language Model. The returnedLlmResponseobject is processed as if it were the actual response from the LLM. Ideal for implementing input guardrails, prompt validation, or serving cached responses.before_tool_callback→dictorMap: Skips the execution of the actual tool function (or sub-agent). The returneddictis used as the result of the tool call, which is then typically passed back to the LLM. Perfect for validating tool arguments, applying policy restrictions, or returning mocked/cached tool results.after_agent_callback→types.Content: Replaces theContentthat the agent's run logic just produced.after_model_callback→LlmResponse: Replaces theLlmResponsereceived from the LLM. Useful for sanitizing outputs, adding standard disclaimers, or modifying the LLM's response structure.after_tool_callback→dictorMap: Replaces thedictresult returned by the tool. Allows for post-processing or standardization of tool outputs before they are sent back to the LLM.
- Returning a specific type of object (instead of
-
return <Specific Object>(覆盖默认行为):- 返回特定类型的对象(而不是
None)是您覆盖 ADK 智能体默认行为的方式。框架将使用您返回的对象并跳过通常跟随的步骤或替换刚刚生成的结果。 before_agent_callback→types.Content: 跳过智能体的主要执行逻辑(_run_async_impl/_run_live_impl)。返回的Content对象立即被视为智能体在这一轮的最终输出。对于直接处理简单请求或强制访问控制很有用。before_model_callback→LlmResponse: 跳过对外部大语言模型的调用。返回的LlmResponse对象被处理,就好像它是来自 LLM 的实际响应一样。非常适合实施输入防护栏、提示验证或提供缓存响应。before_tool_callback→dict或Map: 跳过实际工具函数(或子智能体)的执行。返回的dict用作工具调用的结果,然后通常传递回 LLM。非常适合验证工具参数、应用策略限制或返回模拟/缓存的工具结果。after_agent_callback→types.Content: 替换智能体运行逻辑刚刚生成的Content。after_model_callback→LlmResponse: 替换从 LLM 接收到的LlmResponse。对于清理输出、添加标准免责声明或修改 LLM 的响应结构很有用。after_tool_callback→dict或Map: 替换工具返回的dict结果。允许在工具输出被发送回 LLM 之前进行后处理或标准化。
- 返回特定类型的对象(而不是
Conceptual Code Example (Guardrail):
概念代码示例(防护栏):
This example demonstrates the common pattern for a guardrail using before_model_callback.
此示例演示了使用 before_model_callback 的防护栏的常见模式。
Code
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from typing import Optional
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
GEMINI_2_FLASH="gemini-2.0-flash"
# --- Define the Callback Function ---
def simple_before_model_modifier(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
"""Inspects/modifies the LLM request or skips the call."""
agent_name = callback_context.agent_name
print(f"[Callback] Before model call for agent: {agent_name}")
# Inspect the last user message in the request contents
last_user_message = ""
if llm_request.contents and llm_request.contents[-1].role == 'user':
if llm_request.contents[-1].parts:
last_user_message = llm_request.contents[-1].parts[0].text
print(f"[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '{last_user_message}'")
# --- Modification Example ---
# Add a prefix to the system instruction
original_instruction = llm_request.config.system_instruction or types.Content(role="system", parts=[])
prefix = "[Modified by Callback] "
# Ensure system_instruction is Content and parts list exists
if not isinstance(original_instruction, types.Content):
# Handle case where it might be a string (though config expects Content)
original_instruction = types.Content(role="system", parts=[types.Part(text=str(original_instruction))])
if not original_instruction.parts:
original_instruction.parts.append(types.Part(text="")) # Add an empty part if none exist
# Modify the text of the first part
modified_text = prefix + (original_instruction.parts[0].text or "")
original_instruction.parts[0].text = modified_text
llm_request.config.system_instruction = original_instruction
print(f"[Callback] Modified system instruction to: '{modified_text}'")
# --- Skip Example ---
# Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if "BLOCK" in last_user_message.upper():
print("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.")
# Return an LlmResponse to skip the actual LLM call
return LlmResponse(
content=types.Content(
role="model",
parts=[types.Part(text="LLM call was blocked by before_model_callback.")],
)
)
else:
print("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.")
# Return None to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return None
# Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback
my_llm_agent = LlmAgent(
name="ModelCallbackAgent",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="You are a helpful assistant.", # Base instruction
description="An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback",
before_model_callback=simple_before_model_modifier # Assign the function here
)
APP_NAME = "guardrail_app"
USER_ID = "user_1"
SESSION_ID = "session_001"
# Session and Runner
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=my_llm_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
return session, runner
# Agent Interaction
async def call_agent_async(query):
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
session, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response: ", final_response)
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("write a joke on BLOCK")
/**
* Copyright 2025 Google LLC
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import {
LlmAgent,
InMemoryRunner,
CallbackContext,
isFinalResponse,
} from "@google/adk";
import { createUserContent } from "@google/genai";
const MODEL_NAME = "gemini-2.5-flash";
const APP_NAME = "before_model_callback_app";
const USER_ID = "test_user_before_model";
const SESSION_ID_BLOCK = "session_block_model_call";
const SESSION_ID_NORMAL = "session_normal_model_call";
// --- Define the Callback Function ---
function simpleBeforeModelModifier({
context,
request,
}: {
context: CallbackContext;
request: any;
}): any | undefined {
console.log(`[Callback] Before model call for agent: ${context.agentName}`);
// Inspect the last user message in the request contents
const lastUserMessage = request.contents?.at(-1)?.parts?.[0]?.text ?? "";
console.log(`[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '${lastUserMessage}'`);
// --- Modification Example ---
// Add a prefix to the system instruction.
// We create a deep copy to avoid modifying the original agent's config object.
const modifiedConfig = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(request.config));
const originalInstructionText =
modifiedConfig.systemInstruction?.parts?.[0]?.text ?? "";
const prefix = "[Modified by Callback] ";
modifiedConfig.systemInstruction = {
role: "system",
parts: [{ text: prefix + originalInstructionText }],
};
request.config = modifiedConfig; // Assign the modified config back to the request
console.log(
`[Callback] Modified system instruction to: '${modifiedConfig.systemInstruction.parts[0].text}'`
);
// --- Skip Example ---
// Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if (lastUserMessage.toUpperCase().includes("BLOCK")) {
console.log("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.");
// Return an LlmResponse to skip the actual LLM call
return {
content: {
role: "model",
parts: [
{ text: "LLM call was blocked by the before_model_callback." },
],
},
};
}
console.log("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.");
// Return undefined to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return undefined;
}
// --- Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback ---
const myLlmAgent = new LlmAgent({
name: "ModelCallbackAgent",
model: MODEL_NAME,
instruction: "You are a helpful assistant.", // Base instruction
description: "An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback",
beforeModelCallback: simpleBeforeModelModifier, // Assign the function here
});
// --- Agent Interaction Logic ---
async function callAgentAndPrint(
runner: InMemoryRunner,
query: string,
sessionId: string
) {
console.log(`\n>>> Calling Agent with query: "${query}"`);
let finalResponseContent = "No final response received.";
const events = runner.runAsync({ userId: USER_ID, sessionId, newMessage: createUserContent(query) });
for await (const event of events) {
if (isFinalResponse(event) && event.content?.parts?.length) {
finalResponseContent = event.content.parts
.map((part: { text?: string }) => part.text ?? "")
.join("");
}
}
console.log("<<< Agent Response: ", finalResponseContent);
}
// --- Run Interactions ---
async function main() {
const runner = new InMemoryRunner({ agent: myLlmAgent, appName: APP_NAME });
// Scenario 1: The callback will find "BLOCK" and skip the model call
await runner.sessionService.createSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID_BLOCK,
});
await callAgentAndPrint(
runner,
"write a joke about BLOCK",
SESSION_ID_BLOCK
);
// Scenario 2: The callback will modify the instruction and proceed
await runner.sessionService.createSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID_NORMAL,
});
await callAgentAndPrint(runner, "write a short poem", SESSION_ID_NORMAL);
}
main();
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// onBeforeModelGuardrail is a callback that inspects the LLM request.
// If it contains a forbidden topic, it blocks the request and returns a
// predefined response. Otherwise, it allows the request to proceed.
func onBeforeModelGuardrail(ctx agent.CallbackContext, req *model.LLMRequest) (*model.LLMResponse, error) {
log.Println("--- onBeforeModelGuardrail Callback Triggered ---")
// Inspect the request content for forbidden topics.
for _, content := range req.Contents {
for _, part := range content.Parts {
if strings.Contains(part.Text, "finance") {
log.Println("Forbidden topic 'finance' detected. Blocking LLM call.")
// By returning a non-nil response, we override the default behavior
// and prevent the actual LLM call.
return &model.LLMResponse{
Content: &genai.Content{
Parts: []*genai.Part{{Text: "I'm sorry, but I cannot discuss financial topics."}},
Role: "model",
},
}, nil
}
}
}
log.Println("No forbidden topics found. Allowing LLM call to proceed.")
// Returning nil allows the default LLM call to proceed.
return nil, nil
}
func runGuardrailExample() {
const (
appName = "GuardrailApp"
userID = "test_user_456"
)
ctx := context.Background()
geminiModel, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
agentCfg := llmagent.Config{
Name: "ChatAgent",
Model: geminiModel,
BeforeModelCallbacks: []llmagent.BeforeModelCallback{onBeforeModelGuardrail},
}
chatAgent, err := llmagent.New(agentCfg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: chatAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
import com.google.adk.agents.CallbackContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.events.Event;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmRequest;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmResponse;
import com.google.adk.runner.InMemoryRunner;
import com.google.adk.sessions.Session;
import com.google.genai.types.Content;
import com.google.genai.types.GenerateContentConfig;
import com.google.genai.types.Part;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class BeforeModelGuardrailExample {
private static final String MODEL_ID = "gemini-2.0-flash";
private static final String APP_NAME = "guardrail_app";
private static final String USER_ID = "user_1";
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeforeModelGuardrailExample example = new BeforeModelGuardrailExample();
example.defineAgentAndRun("Tell me about quantum computing. This is a test.");
}
// --- Define your callback logic ---
// Looks for the word "BLOCK" in the user prompt and blocks the call to LLM if found.
// Otherwise the LLM call proceeds as usual.
public Optional<LlmResponse> simpleBeforeModelModifier(
CallbackContext callbackContext, LlmRequest llmRequest) {
System.out.println("[Callback] Before model call for agent: " + callbackContext.agentName());
// Inspect the last user message in the request contents
String lastUserMessageText = "";
List<Content> requestContents = llmRequest.contents();
if (requestContents != null && !requestContents.isEmpty()) {
Content lastContent = requestContents.get(requestContents.size() - 1);
if (lastContent.role().isPresent() && "user".equals(lastContent.role().get())) {
lastUserMessageText =
lastContent.parts().orElse(List.of()).stream()
.flatMap(part -> part.text().stream())
.collect(Collectors.joining(" ")); // Concatenate text from all parts
}
}
System.out.println("[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '" + lastUserMessageText + "'");
String prefix = "[Modified by Callback] ";
GenerateContentConfig currentConfig =
llmRequest.config().orElse(GenerateContentConfig.builder().build());
Optional<Content> optOriginalSystemInstruction = currentConfig.systemInstruction();
Content conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction;
if (optOriginalSystemInstruction.isPresent()) {
Content originalSystemInstruction = optOriginalSystemInstruction.get();
List<Part> originalParts =
new ArrayList<>(originalSystemInstruction.parts().orElse(List.of()));
String originalText = "";
if (!originalParts.isEmpty()) {
Part firstPart = originalParts.get(0);
if (firstPart.text().isPresent()) {
originalText = firstPart.text().get();
}
originalParts.set(0, Part.fromText(prefix + originalText));
} else {
originalParts.add(Part.fromText(prefix));
}
conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction =
originalSystemInstruction.toBuilder().parts(originalParts).build();
} else {
conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction =
Content.builder()
.role("system")
.parts(List.of(Part.fromText(prefix)))
.build();
}
// This demonstrates building a new LlmRequest with the modified config.
llmRequest =
llmRequest.toBuilder()
.config(
currentConfig.toBuilder()
.systemInstruction(conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction)
.build())
.build();
System.out.println(
"[Callback] Conceptually modified system instruction is: '"
+ llmRequest.config().get().systemInstruction().get().parts().get().get(0).text().get());
// --- Skip Example ---
// Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if (lastUserMessageText.toUpperCase().contains("BLOCK")) {
System.out.println("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.");
LlmResponse skipResponse =
LlmResponse.builder()
.content(
Content.builder()
.role("model")
.parts(
List.of(
Part.builder()
.text("LLM call was blocked by before_model_callback.")
.build()))
.build())
.build();
return Optional.of(skipResponse);
}
System.out.println("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.");
// Return Optional.empty() to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return Optional.empty();
}
public void defineAgentAndRun(String prompt) {
// --- Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback ---
LlmAgent myLlmAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("ModelCallbackAgent")
.model(MODEL_ID)
.instruction("You are a helpful assistant.") // Base instruction
.description("An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback")
.beforeModelCallbackSync(this::simpleBeforeModelModifier) // Assign the callback here
.build();
// Session and Runner
InMemoryRunner runner = new InMemoryRunner(myLlmAgent, APP_NAME);
// InMemoryRunner automatically creates a session service. Create a session using the service
Session session = runner.sessionService().createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID).blockingGet();
Content userMessage =
Content.fromParts(Part.fromText(prompt));
// Run the agent
Flowable<Event> eventStream = runner.runAsync(USER_ID, session.id(), userMessage);
// Stream event response
eventStream.blockingForEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse()) {
System.out.println(event.stringifyContent());
}
});
}
}
By understanding this mechanism of returning None versus returning specific objects, you can precisely control the agent's execution path, making callbacks an essential tool for building sophisticated and reliable agents with ADK.